Micro-lattice : The lightest metal ever!!
Welcome Readers, here we are with another mind-blowing blog for you.
Material Science is the most evolving field in this era. In Today’s world sustainable development are the goal of every scientific research, manufacturer, government, and private companies. Supplementary materials which are required to achieve this goal are being invented day by day and we are going even closer to it. Aerospace Industry is such a field that demand the lightest and strongest metals for decades. Aluminum has fulfilled this demand to some extent, but not fully. MICROLATTICE is one such material, set to make a revolution in the industry.
What is Micro-lattice?
A lattice whose dimensions are close to the micrometer scale is called a micro-lattice. These are periodic cellular structures, where lattice formation occurs due to interconnected struts.
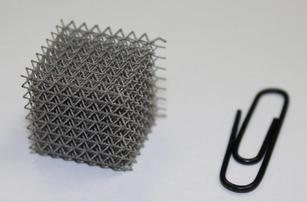 |
| Image source: https://www.insidemetaladditivemanufacturing.com/blog/metallic-microlattices-and-applications |
What Makes Micro-lattice Unique?
Micro-lattice, developed by Boeing’s HRL Laboratories along with colleagues at the University of California and the California Institute of Technology. What it calls ‘The Lightest Metal Ever’, is constructed with 99.99% Air.
 |
| Image source: https://www.dezeen.com/2015/10/15/microlattice-metal-worlds-lightest-material-boeing-movie/ |
Micro-lattice’s structure is inspired from open cellular structure of our bones. The outside of bones is very rigid but inside is hollow. Micro-lattice is also a 3D open cellular polymer structure which makes it lightweight and tough. Having an ultra-low density, Micro-lattice can recover from compressions exceeding 50% strain and also is able to absorb an incredible amount of energy. It’s light enough to balance it on top of a dandelion, while its structure makes it strong. Strength and record-breaking lightness make it a future metal for future airplanes and vehicles.
Microlattice: Lightest. Metal. Ever.
Manufacturing Process:
A two-dimensional mask with a pattern of apertures covering a photo-monomer reservoir is exposed to collimated UV light. Within the photo-monomer, self-propagating photopolymer waveguides originate at each aperture in the direction of the UV collimated beam and polymerize together at points of intersection. By simultaneously forming an interconnected array of these fibers in three dimensions and removing the uncured monomer, unique three-dimensional lattice-based open cellular polymer materials can be rapidly fabricated. Polymer Micro-lattices can be converted into a variety of materials, including metals and ceramics. The polymer lattice can be used as a template or scaffold for electro and electroless plating or thin-film deposition. After deposition, the polymer is chemically removed or away leaving behind a hollow, thin-walled light structure.
Applications:
· It was originally developed for Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA)
· It finds its main application in the aerospace industry due to its lightweight nature.
· They can be used in applications like thermal and vibration insulators like shock absorbers.
· Sandwich beams and panels
· Energy absorption
Recent developments in the field of micro-lattice:
1. Additive manufacturing technology is being used for manufacturing micro lattice such as 3D printing a metallic micro-lattice. The mechanical behavior of the micro-lattice can be altered by changing its structural density and by making simple changes in its cell architecture.
2. With the help of additive manufacturing, this lightweight technology now can accommodate geometrically intricate parts and complex assemblies. Also, it results in rapid, simple, and scalable fabrication of micro-lattice.
3. It is becoming popular in industrial applications like medical and bioengineering, aviation, automation, and robotics. It is believed to be useful in developing engineering systems such as lightweight high-strength materials, materials with controlled deformation, fast-charging high-capacity Li-ion batteries, biomedical implants, catalysts, and micro-filters.
4. One of the applications called micro-lattice heat pipe is proposed to be used in electric vehicles for the battery thermal management system which improves the performance of the vehicles
5. The traditional radiators in cars are being replaced by the micro-lattice heat exchangers because of the energy absorption capacity of the micro-lattice structure the damage to the radiator can be prevented in case of any car accidents.
BLOG CREDITS: MADHURA MAHAMUNI TY METALLURGY MIS 111911024
CHETANESHWARI NIVARGI TY METALLURGY MIS 111911009
VEDANT LONDHE TY METALLURGY MIS 111911058
References:
1) https://www.boeing.com/features/2015/10/innovation-lightest-metal-10-15.page
2) Architected Microlattice Materials by Self-Propagating Waveguide Processing L. Corrion, E. Clough, Z. Eckel, J. Hundley, C. Roper, T. Schaedler, HRL Laboratories, LLC
3)https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317703251_Architected_Microlattice_Materials_by_Self-Propagating_Waveguide_Processing
4) https://www.dezeen.com/2015/10/15/microlattice-metal-worlds-lightest-material-boeing-movie/
5) https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13369-021-05992-y
6) https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221486042100021X
7) https://engj.org/index.php/ej/article/view/3524/913 -
8) (Swapnil Narkhedea , Anirban Surb,* , and Sanjay Darvekar.2019. Applications, Manufacturing and Thermal Characteristics of MicroLattice Structures: Current State of the Art. ENGINEERING JOURNAL. Volume 23. Issue 6:428.)





Comments
Post a Comment